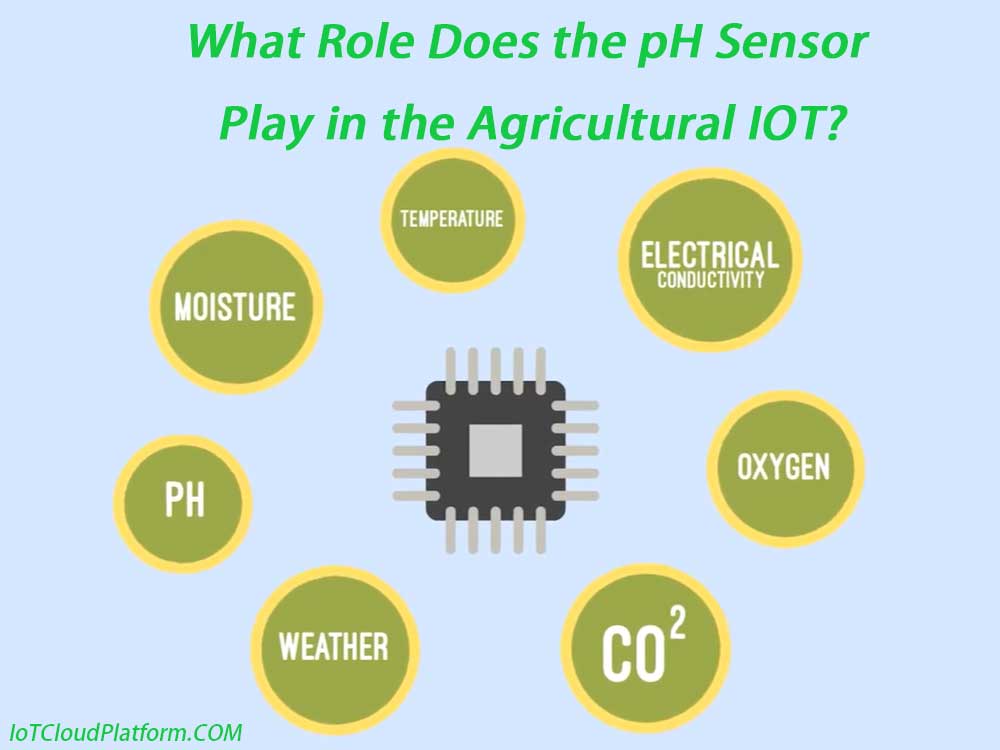
What Role Does the pH Sensor Play in the Agricultural IOT?
The pH sensor plays a vital role in the agricultural Internet of Things. As an important part of the intelligent agricultural system, it provides accurate data support for agricultural production by real-time monitoring of the pH value (pH value) of soil or water quality, and helps the refined management and sustainable development of agricultural production.
The following is a detailed introduction to the role of pH sensors in the agricultural Internet of Things:
Basic principles of pH sensors
The pH sensor is a sensor based on electrochemical principles, mainly composed of a glass indicator electrode and a reference electrode.
By measuring the potential difference generated by the working battery in the solution, the linear relationship between the pH value of the solution to be tested and the potential of the working battery is used to achieve online monitoring of pH.
This sensor has good repeatability and stability, and has an automatic temperature compensation function, which can ensure the accuracy of the measurement results.
Application of pH sensors in the agricultural Internet of Things
Real-time monitoring of soil pH
The growth of crops requires a suitable soil pH environment. Excessively acidic or alkaline soils will inhibit the growth of crops and even cause crop death. PH sensors can monitor the pH of the soil in real time and transmit data to the agricultural IoT platform. Farmers can remotely view soil pH data through mobile phones or computers. Based on these data, farmers can adjust the soil pH in time to provide the best growth environment for crops.
Precision Fertilization Guidance
Traditional fertilization methods are often blind and wasteful. Excessive fertilization not only increases agricultural production costs, but may also lead to soil pollution and eutrophication of water bodies. When the PH sensor is combined with the agricultural IoT system, the required fertilizer type and amount can be accurately calculated based on the soil pH and the crop’s demand for nutrients. This precise fertilization method helps reduce fertilizer waste, improve fertilizer utilization, and reduce environmental pollution.
Intelligent Irrigation Management
Crops need sufficient water to grow, but excessive irrigation will lead to waste of water resources and accumulation of soil salt. While monitoring soil pH, the PH sensor can also be combined with equipment such as soil moisture sensors to achieve intelligent irrigation management.
When the soil moisture is below a certain threshold, the system will automatically start the irrigation equipment; when the soil moisture and pH both reach the appropriate range, the system will automatically stop irrigation. This intelligent irrigation method helps save water resources and improve irrigation efficiency.
Improvement of agricultural product quality
The quality of agricultural products is closely related to their growth environment. Through real-time monitoring and data analysis of pH sensors, farmers can more accurately control the growth environment of crops, including soil pH, water and nutrients. This refined management helps to improve the quality of agricultural products and increase the added value and market competitiveness of agricultural products.
Agricultural production decision support
The agricultural Internet of Things platform aggregates and analyzes the data collected by devices such as pH sensors to form big data for agricultural production. These data can not only help farmers formulate more scientific and reasonable production plans and management plans, but also provide decision support for government departments.
For example, government departments can formulate corresponding soil improvement measures and environmental protection policies based on soil pH data to promote the sustainable development of agriculture.
Technical features of pH sensors
High-precision measurement
The pH sensor adopts advanced electrochemical measurement technology and has the characteristics of high precision and high stability. Its measurement range is wide and can meet the pH measurement needs under different soil types and water conditions.
Automatic temperature compensation
The pH sensor has an automatic temperature compensation function, which can automatically correct the effect of temperature on the measurement results. This function ensures the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results at different temperatures.
Digital output
Modern pH sensors support digital output (such as RS485, MODBUS/RTU, etc.), which can be easily connected and integrated with the agricultural Internet of Things system. Digital output not only improves the efficiency and accuracy of data transmission, but also reduces signal interference and transmission costs.
Easy to install and maintain
The pH sensor has a reasonable structural design and is easy and quick to install. At the same time, its cleaning and activation are simple, the balancing speed is fast, and the maintenance cost is low. This makes pH sensors widely used and promoted in the agricultural Internet of Things.
Summary and Outlook
In summary, pH sensors play an irreplaceable role in the agricultural Internet of Things. By real-time monitoring of the pH data of soil or water quality, it provides accurate data support and management decision-making basis for agricultural production.
With the continuous development and progress of science and technology, the application of pH sensors in agricultural Internet of Things will become more and more extensive and in-depth.
In the future, we can expect the introduction and integration of more advanced technologies and equipment to promote the development of agricultural Internet of Things in a more intelligent, precise and efficient direction.
At the same time, governments, enterprises, scientific research institutions and other parties should strengthen cooperation and exchanges to jointly promote the innovation and development of agricultural Internet of Things technology and contribute more wisdom and strength to the sustainable development of agricultural production.
IOT Cloud Platform
IOT Cloud Platform is an IoT portal established by a Chinese IoT company, focusing on technical solutions in the fields of agricultural IoT, industrial IoT, medical IoT, security IoT, military IoT, meteorological IoT, consumer IoT, automotive IoT, commercial IoT, infrastructure IoT, smart warehousing and logistics, smart home, smart city, smart healthcare, smart lighting, etc.
The IoT Cloud Platform blog is a top IoT technology stack, providing technical knowledge on IoT, robotics, artificial intelligence (generative artificial intelligence AIGC), edge computing, AR/VR, cloud computing, quantum computing, blockchain, smart surveillance cameras, drones, RFID tags, gateways, GPS, 3D printing, 4D printing, autonomous driving, etc.