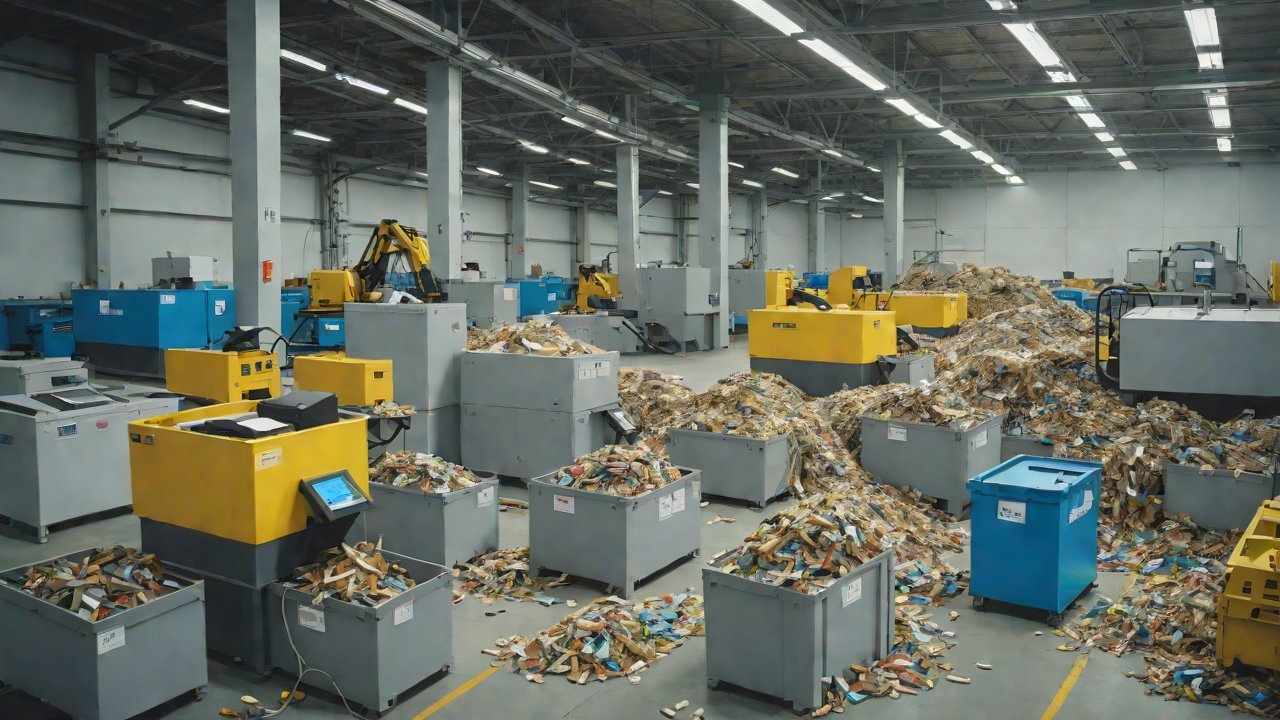
Waste Sorting 2.0: Recycling Solution Based on Image Recognition and IoT Weighing
The world’s waste management systems are at a crossroads, where decades of inefficiencies have led to an unprecedented crisis. The global recycling rate has stagnated, with a staggering 40% of municipal solid waste ending up in landfills or incinerators. Amidst this backdrop, innovation is being driven by the convergence of image recognition and IoT weighing technologies, which promise to transform the waste sorting process.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors enables real-time monitoring and analysis of waste composition, allowing for more accurate and efficient sorting. This approach not only reduces contamination rates but also minimizes the manual labor required in traditional recycling facilities. Furthermore, it empowers local governments to make data-driven decisions regarding waste management policies.
1. Market Overview
The global waste management market is projected to reach $2.3 trillion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%. However, the current manual sorting process is not only inefficient but also unsustainable. The introduction of AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies has the potential to disrupt this market, with estimates suggesting that it could capture up to 20% of the global waste management share.
| Market Segment | Current Size (2022) | Projected Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Municipal Solid Waste Management | $1.3 trillion | 7.5% CAGR |
| Industrial Waste Management | $530 billion | 6.2% CAGR |
| Hazardous Waste Management | $230 billion | 8.1% CAGR |
2. Technological Advancements
Image recognition technology plays a crucial role in the waste sorting process, as it enables the identification of recyclable materials such as plastics, paper, and glass. Advanced computer vision algorithms can detect even small contaminants, reducing contamination rates by up to 50%. Furthermore, these systems can be integrated with existing infrastructure, minimizing the need for costly upgrades.
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| AI-powered Image Recognition | Real-time identification of recyclable materials |
| IoT Weighing Sensors | Accurate measurement of waste composition and weight |
3. Benefits and Challenges
The adoption of Waste Sorting 2.0 has numerous benefits, including:
- Improved recycling rates
- Reduced contamination rates
- Increased efficiency in waste sorting processes
- Enhanced decision-making capabilities for local governments
However, there are also challenges to be addressed:
- High upfront costs associated with implementing AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies
- Data security concerns regarding the storage and transmission of sensitive information
- Potential job displacement in traditional recycling facilities
4. Case Studies and Examples
Several cities have already implemented Waste Sorting 2.0, with promising results:
- San Francisco’s Zero-Waste Plan: The city aims to reduce its waste output by 80% by 2030, leveraging AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies to achieve this goal.
- New York City’s Recycling Program: The Big Apple has implemented a city-wide recycling program that uses AI-powered image recognition to sort recyclables from non-recyclables.
5. Market Players and Partnerships
Several companies are already investing in Waste Sorting 2.0, with partnerships emerging between technology providers and waste management companies:
- Waste Management Inc.’s Partnership with Microsoft: The partnership aims to integrate AI-powered image recognition into Waste Management’s existing recycling facilities.
- Veolia Environnement’s Investment in IoT Weighing Technology: Veolia has invested heavily in IoT weighing sensors, which are being integrated into its waste management facilities worldwide.
6. Conclusion
Waste Sorting 2.0 has the potential to revolutionize the global waste management industry by leveraging AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies. While there are challenges to be addressed, the benefits of improved recycling rates, reduced contamination rates, and increased efficiency in waste sorting processes make this approach a promising solution for a more sustainable future.
7. Recommendations
To accelerate the adoption of Waste Sorting 2.0, we recommend:
- Increased investment in AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies
- Collaboration between technology providers and waste management companies to develop cost-effective solutions
- Development of data standards and protocols for secure data transmission and storage

The world’s waste management systems are at a crossroads, where decades of inefficiencies have led to an unprecedented crisis. The global recycling rate has stagnated, with a staggering 40% of municipal solid waste ending up in landfills or incinerators. Amidst this backdrop, innovation is being driven by the convergence of image recognition and IoT weighing technologies, which promise to transform the waste sorting process.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors enables real-time monitoring and analysis of waste composition, allowing for more accurate and efficient sorting. This approach not only reduces contamination rates but also minimizes the manual labor required in traditional recycling facilities. Furthermore, it empowers local governments to make data-driven decisions regarding waste management policies.
1. Market Overview
The global waste management market is projected to reach $2.3 trillion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%. However, the current manual sorting process is not only inefficient but also unsustainable. The introduction of AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies has the potential to disrupt this market, with estimates suggesting that it could capture up to 20% of the global waste management share.
| Market Segment | Current Size (2022) | Projected Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Municipal Solid Waste Management | $1.3 trillion | 7.5% CAGR |
| Industrial Waste Management | $530 billion | 6.2% CAGR |
| Hazardous Waste Management | $230 billion | 8.1% CAGR |
2. Technological Advancements
Image recognition technology plays a crucial role in the waste sorting process, as it enables the identification of recyclable materials such as plastics, paper, and glass. Advanced computer vision algorithms can detect even small contaminants, reducing contamination rates by up to 50%. Furthermore, these systems can be integrated with existing infrastructure, minimizing the need for costly upgrades.
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| AI-powered Image Recognition | Real-time identification of recyclable materials |
| IoT Weighing Sensors | Accurate measurement of waste composition and weight |
3. Benefits and Challenges
The adoption of Waste Sorting 2.0 has numerous benefits, including:
- Improved recycling rates
- Reduced contamination rates
- Increased efficiency in waste sorting processes
- Enhanced decision-making capabilities for local governments
However, there are also challenges to be addressed:
- High upfront costs associated with implementing AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies
- Data security concerns regarding the storage and transmission of sensitive information
- Potential job displacement in traditional recycling facilities
4. Case Studies and Examples
Several cities have already implemented Waste Sorting 2.0, with promising results:
- San Francisco’s Zero-Waste Plan: The city aims to reduce its waste output by 80% by 2030, leveraging AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies to achieve this goal.
- New York City’s Recycling Program: The Big Apple has implemented a city-wide recycling program that uses AI-powered image recognition to sort recyclables from non-recyclables.
5. Market Players and Partnerships
Several companies are already investing in Waste Sorting 2.0, with partnerships emerging between technology providers and waste management companies:
- Waste Management Inc.’s Partnership with Microsoft: The partnership aims to integrate AI-powered image recognition into Waste Management’s existing recycling facilities.
- Veolia Environnement’s Investment in IoT Weighing Technology: Veolia has invested heavily in IoT weighing sensors, which are being integrated into its waste management facilities worldwide.
6. Conclusion
Waste Sorting 2.0 has the potential to revolutionize the global waste management industry by leveraging AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies. While there are challenges to be addressed, the benefits of improved recycling rates, reduced contamination rates, and increased efficiency in waste sorting processes make this approach a promising solution for a more sustainable future.
7. Recommendations
To accelerate the adoption of Waste Sorting 2.0, we recommend:
- Increased investment in AI-powered image recognition and IoT weighing technologies
- Collaboration between technology providers and waste management companies to develop cost-effective solutions
- Development of data standards and protocols for secure data transmission and storage
IOT Cloud Platform
IOT Cloud Platform is an IoT portal established by a Chinese IoT company, focusing on technical solutions in the fields of agricultural IoT, industrial IoT, medical IoT, security IoT, military IoT, meteorological IoT, consumer IoT, automotive IoT, commercial IoT, infrastructure IoT, smart warehousing and logistics, smart home, smart city, smart healthcare, smart lighting, etc.
The IoT Cloud Platform blog is a top IoT technology stack, providing technical knowledge on IoT, robotics, artificial intelligence (generative artificial intelligence AIGC), edge computing, AR/VR, cloud computing, quantum computing, blockchain, smart surveillance cameras, drones, RFID tags, gateways, GPS, 3D printing, 4D printing, autonomous driving, etc.