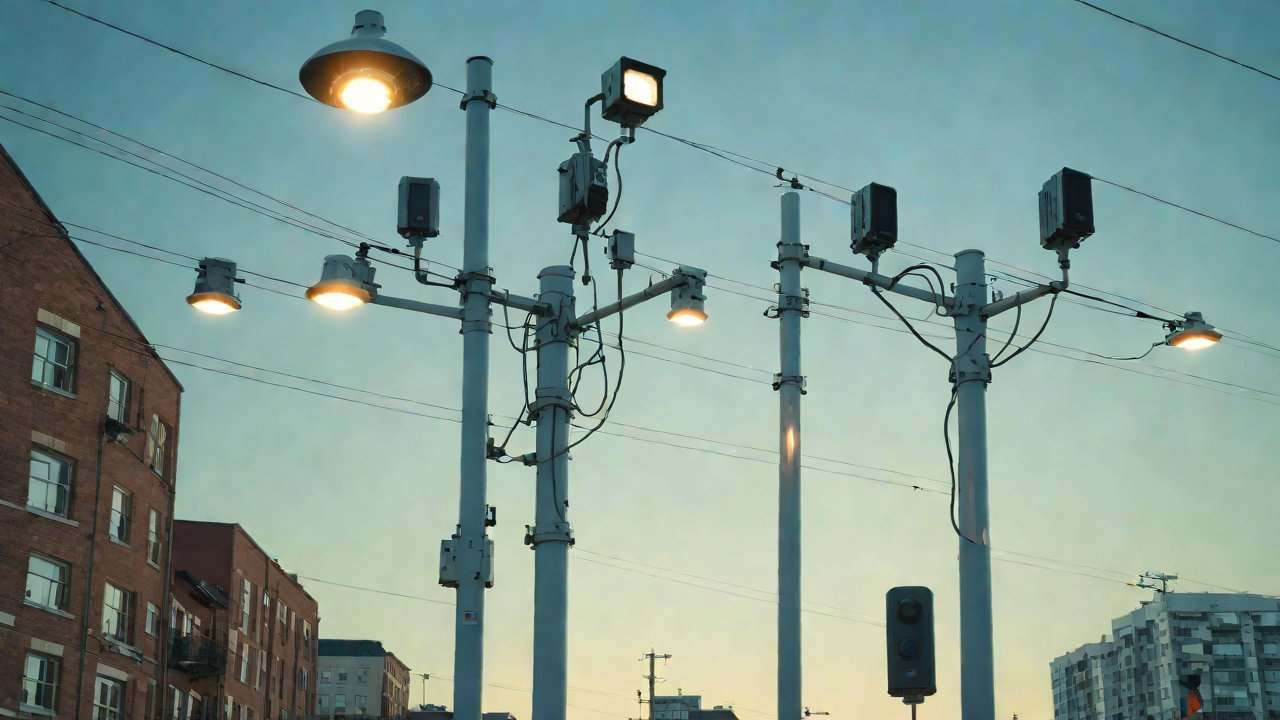
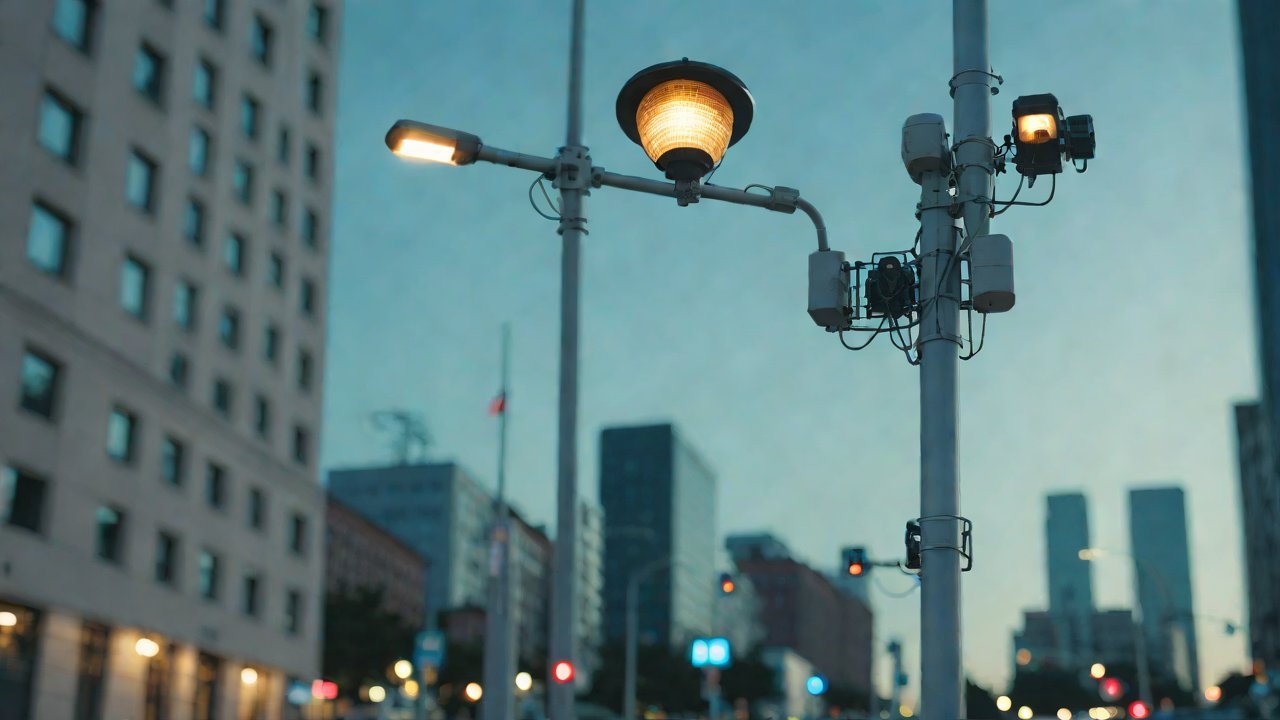
Integration of 5G Micro Base Stations with Streetlight Pole Physical Space and Electromagnetic Interference
The advent of 5G technology has brought about a paradigm shift in wireless communication, enabling faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and increased connectivity. However, its integration with existing infrastructure poses significant challenges, particularly in urban areas where space is limited and electromagnetic interference (EMI) is high. One potential solution lies in the strategic placement of 5G micro base stations on streetlight poles, which offer a unique combination of physical space and accessibility.
1. Market Overview
The global market for 5G infrastructure is projected to grow at an unprecedented rate, with estimates suggesting it will reach $667 billion by 2028 (Source: MarketsandMarkets). The increasing demand for high-speed data transfer and low-latency communication has driven the development of innovative solutions, including the integration of 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles. This approach not only optimizes the use of existing infrastructure but also reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional cell tower installations.
| Region | 2022 Market Size (USD billion) | 2028 CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 12.3 | 25.6% |
| Europe | 13.5 | 24.1% |
| Asia-Pacific | 23.7 | 26.4% |
| Latin America | 2.1 | 22.9% |
| Middle East and Africa | 1.8 | 20.3% |
2. Technical Considerations
The integration of 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles requires careful consideration of several technical factors, including:
- EMI Mitigation: Streetlights can generate significant EMI due to their proximity to electrical sources and the presence of other wireless devices in the vicinity. Advanced shielding techniques and antenna design are essential to minimize interference.
- Physical Space Optimization: The compact size of 5G micro base stations necessitates efficient use of streetlight pole space, often requiring innovative mounting solutions and compact enclosure designs.
- Power Supply and Cooling: Streetlights typically have limited power capacity, which can impact the performance of integrated 5G equipment. Efficient power supply systems and cooling mechanisms are essential to ensure reliable operation.

| Technical Parameter | Typical Value (5G Micro Base Station) | Typical Value (Streetlight Pole) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 24 GHz – 39 GHz | N/A |
| Power Consumption | 500 W – 1000 W | 50 W – 200 W |
| Cooling Mechanism | Air-cooled or liquid-cooled | Passive cooling |
3. Antenna Design and Placement
The placement of antennas on streetlight poles is critical to ensure optimal signal coverage and minimize EMI. Factors influencing antenna design and placement include:
- Polarization: Vertical polarization is often preferred for streetlight pole installations due to its ability to mitigate EMI from adjacent sources.
- Directionality: Sectorized or omnidirectional antennas can be used, depending on the specific requirements of the network and the surrounding environment.
- Mounting Arrangements: Antennas may be mounted directly onto the streetlight pole or attached to a separate mast for improved accessibility.
| Antenna Configuration | Typical Gain (dBi) | Typical Beamwidth (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Sectorized Antenna | 18 – 22 dBi | 60° – 120° |
| Omnidirectional Antenna | 12 – 16 dBi | 360° |
4. Electromagnetic Interference Mitigation
EMI is a significant concern when integrating 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles, particularly in urban areas where multiple wireless devices coexist. Strategies for mitigating EMI include:
- Shielding: Using advanced shielding materials or designs to minimize electromagnetic radiation.
- Frequency Planning: Carefully planning frequency allocation to avoid conflicts between different wireless systems.
- Antenna Design: Optimizing antenna design to minimize EMI and ensure efficient signal transmission.
| Shielding Material | Typical Thickness (mm) | Typical Attenuation (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 1.5 – 3 mm | 10 – 20 dB |
| Copper | 2.5 – 4 mm | 15 – 30 dB |
5. Case Studies and Implementation Examples
Several cities worldwide have successfully integrated 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles, demonstrating the effectiveness of this approach in optimizing infrastructure utilization and reducing EMI. Notable examples include:
- Singapore: The city-state has implemented a comprehensive smart lighting system that incorporates 5G micro base stations on streetlight poles, providing high-speed connectivity for IoT devices.
- Tokyo: Tokyo’s metropolitan government has partnered with telecommunications operators to deploy 5G micro base stations on streetlight poles, enhancing public safety and emergency services.
| City | Implementation Year | Number of Integrated Sites |
|---|---|---|
| Singapore | 2020 | 500+ |
| Tokyo | 2019 | 1000+ |
6. Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Initiatives
Regulatory frameworks and policy initiatives play a crucial role in facilitating the integration of 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles. Governments worldwide are implementing policies to support the deployment of 5G infrastructure, including:
- Spectrum Allocation: Governments are allocating specific spectrum bands for 5G use cases, ensuring efficient frequency planning.
- Infrastructure Sharing: Policies promoting infrastructure sharing between operators can optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
| Country | Regulatory Framework | Policy Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FCC’s Spectrum Auctions | Infrastructure Sharing Act |
| EU | European Commission’s 5G Action Plan | Net Neutrality Regulation |
The integration of 5G micro base stations with streetlight poles offers a promising solution for optimizing infrastructure utilization and mitigating EMI in urban areas. As the global market for 5G infrastructure continues to grow, it is essential to address technical, regulatory, and policy challenges through collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, governments, and research institutions.
IOT Cloud Platform
IOT Cloud Platform is an IoT portal established by a Chinese IoT company, focusing on technical solutions in the fields of agricultural IoT, industrial IoT, medical IoT, security IoT, military IoT, meteorological IoT, consumer IoT, automotive IoT, commercial IoT, infrastructure IoT, smart warehousing and logistics, smart home, smart city, smart healthcare, smart lighting, etc.
The IoT Cloud Platform blog is a top IoT technology stack, providing technical knowledge on IoT, robotics, artificial intelligence (generative artificial intelligence AIGC), edge computing, AR/VR, cloud computing, quantum computing, blockchain, smart surveillance cameras, drones, RFID tags, gateways, GPS, 3D printing, 4D printing, autonomous driving, etc.