2026 Underwater Archaeology: 3D Scanning and IoT-Based Site Protection Solution
As we embark on a new decade, humanity’s fascination with our submerged past continues to grow, driven by technological advancements that enable us to explore and preserve underwater archaeological sites with unprecedented precision. The 2020s have witnessed a significant surge in the adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), and Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) for site mapping, excavation, and documentation. However, these innovations also pose challenges related to data management, interpretation, and protection of sensitive sites.
Underwater archaeological sites are fragile ecosystems that require specialized care to prevent damage from human activities or natural disasters. The increasing number of underwater excavations has led to a pressing need for robust site protection solutions that can detect potential threats in real-time and respond accordingly. This report delves into the world of 3D scanning and IoT-based site protection, exploring how these technologies can safeguard our submerged cultural heritage.
1. Underwater Archaeology: A Growing Discipline
Underwater archaeology has become a significant area of study over the past few decades, with numerous discoveries shedding light on human history, particularly in regions where sea levels have risen or fallen due to climate changes. The significance of underwater archaeological sites lies not only in their ability to provide insights into past civilizations but also in preserving cultural heritage for future generations.
The use of advanced technologies has transformed the field of underwater archaeology. AUVs and ROVs equipped with high-resolution sensors and cameras enable researchers to map, excavate, and document sites more efficiently than ever before. These vehicles can collect data on water temperature, salinity, and currents, which is crucial for understanding site conditions.
Table 1: Notable Underwater Archaeological Discoveries
| Year | Site Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Uluburun Shipwreck, Turkey | Ancient cargo ship dating back to the 14th century BC |
| 2018 | Antikythera Wreck, Greece | Greek vessel carrying a sophisticated astronomical calculator |
| 2020 | Thonis-Heraklion, Egypt | Lost city submerged in the Mediterranean due to earthquakes and floods |
2. Challenges in Underwater Archaeology
While technological advancements have improved our ability to explore and document underwater sites, several challenges persist:
- Data Management: The sheer volume of data generated by AUVs and ROVs can be overwhelming for researchers to process and analyze.
- Site Protection: As more sites are discovered, the need for robust protection mechanisms increases. Current methods often rely on manual monitoring, which is time-consuming and may not detect threats in real-time.
- Funding: Underwater archaeology projects often face funding constraints due to their complexity and the specialized equipment required.
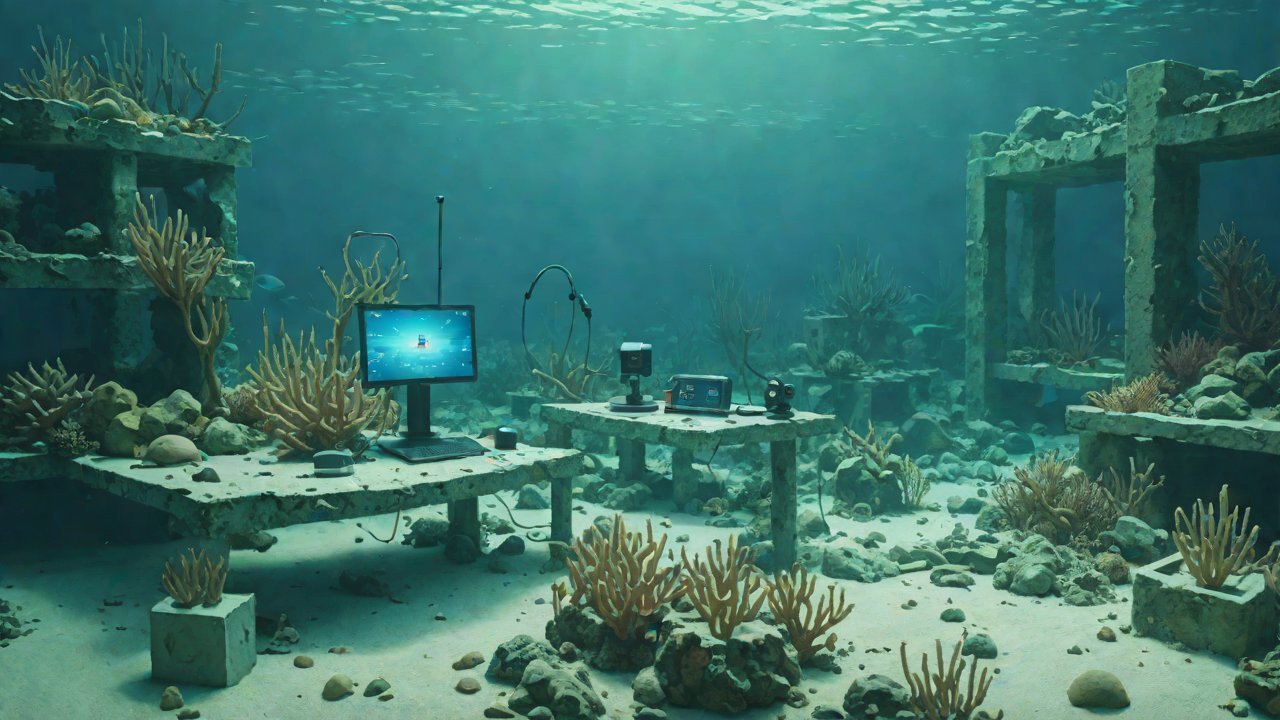
3. IoT-Based Site Protection Solutions
IoT technology offers a promising solution for site protection by enabling real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, detecting potential threats, and triggering responses to prevent damage.
Table 2: Components of an IoT-Based Site Protection System
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensors | High-resolution sensors to monitor water temperature, salinity, currents, and other environmental factors. |
| Data Processing Unit | Analyzes data from sensors in real-time, detecting anomalies that may indicate potential threats. |
| Communication Module | Enables secure communication between the site protection system and remote monitoring centers or emergency services. |
| Actuation System | Triggers responses to detected threats, such as alerting authorities or activating protective barriers. |
4. Integration with 3D Scanning Technologies
Combining IoT-based site protection with 3D scanning technologies can provide a comprehensive solution for underwater archaeological sites:
- Real-time Site Monitoring: IoT sensors and data processing units enable real-time monitoring of site conditions, ensuring that any potential threats are detected promptly.
- High-Resolution Mapping: 3D scanning technologies create detailed maps of the site, enabling researchers to identify areas of interest and track changes over time.
Table 3: Benefits of Integrating IoT and 3D Scanning Technologies
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Site Protection | Real-time monitoring and detection of potential threats. |
| Improved Data Management | High-resolution maps enable efficient data collection, analysis, and interpretation. |
| Increased Efficiency | Automation reduces manual labor required for site documentation and protection. |
5. Future Outlook
As we look to the future, it is clear that the integration of IoT-based site protection with 3D scanning technologies will play a pivotal role in safeguarding underwater archaeological sites:
- Advancements in Sensor Technology: Improved sensor accuracy and range will enable more effective monitoring of site conditions.
- Increased Adoption of IoT: Widespread adoption of IoT technology in various industries will drive down costs, making it more accessible for underwater archaeology projects.
- Enhanced Data Analysis Tools: Advancements in data processing and analysis software will facilitate the interpretation of complex datasets.
The preservation of our submerged cultural heritage is a collective responsibility. By embracing cutting-edge technologies like 3D scanning and IoT-based site protection solutions, we can ensure that these irreplaceable sites remain safe for future generations to study and appreciate.
IOT Cloud Platform
IOT Cloud Platform is an IoT portal established by a Chinese IoT company, focusing on technical solutions in the fields of agricultural IoT, industrial IoT, medical IoT, security IoT, military IoT, meteorological IoT, consumer IoT, automotive IoT, commercial IoT, infrastructure IoT, smart warehousing and logistics, smart home, smart city, smart healthcare, smart lighting, etc.
The IoT Cloud Platform blog is a top IoT technology stack, providing technical knowledge on IoT, robotics, artificial intelligence (generative artificial intelligence AIGC), edge computing, AR/VR, cloud computing, quantum computing, blockchain, smart surveillance cameras, drones, RFID tags, gateways, GPS, 3D printing, 4D printing, autonomous driving, etc.